0 Web 2.0 and CMS
0.1 Web History
After years of email prevalence, now the Web is the most used service provided by Internet. It is an evolving environment, characterizing the IT business and its economy. Up to now, three phases have been identified:
|
Ver. |
Years |
Mode |
Schema |
Front-End |
|
|
1.0 |
1980s |
r-- |
Actors: · WebMaster · Internet Surfers
|
Text (80x2)
|
Graphic (640x480)
|
|
2.0 |
2000s |
Rw- |
Actors: · WebMaster/ Social Media · Internet Surfers/Contributors
|
Cooperation
|
Graphic (adaptable)
|
|
3.0 |
2020s |
rwx |
Actors: · WebMaster/Social Media · Internet Surfers/Contributors · WebHost/Semantic Server
|
Automatic Functions:
· Semantic Markup: communication gap between human web users and computerized applications (provide context to data) · Web Services: software system designed to support computer-to-computer interaction over the Internet · Vectoring: Scalable Vector Graphics (adapt to different devices) |
Concepts:
· Tim Berners Lee (Wikipedia) · Kate Ray (flatworldbusiness) |
Different access level are allowed. The contents could be organized based on types (Static, Article, Image, etc).
0.2 Web 2.0 Architecture
The CMS is an infrastructural layer, offering the following advantages:
· Interface: the user choose the information (text, images, videos) to display, interacting with the website, according to specific actions (e.g. click, sting insertion).
· Protocol: it acts like a buffer, uncoupling the information from the way these are displayed. This allow for a more dynamic content uploads and modifications
· Service: it organize the content, structuring the information along the web interface
0.2.1 CMS: Logical Schema
The web 2.0 is intimal intertwined with CMS, since most parts of vulnerable Web 2.0 are built around a Content Management System, in order to take advantage of the new web experience:
· Same same: unique interface for all the site-operations (reading, writing, configuring, etc)
· But different: separation between the content and how it is shown to the user
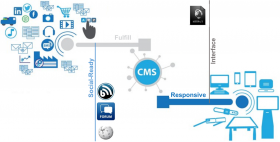
By the means of only one interface: HTTP (1.1), uncoupling interface, aspect and content. The following picture depicts the CMS addressing its tasks:
Figure 1- CMS: Logical Schema
The following definitions are used in the picture:
· Social-Ready: Accepting content from users and usual web-places
· CMS: Managing Content (Collecting, Elaborating, Harvesting, Presenting)
· Interface: Picturing content depending on used media device
0.2.2 CMS: Communication Schema
According to [11], only 38,6% of Web Sites make use of a CMS infrastructure (that is, 61.4% are more than static website).
The information are no more static, these are collected, elaborated and presented depending on user input. The following actions are performed orderly:
· retrieving input (link follow, form fill)
· translating input as punctual queries to perform interrogation
· accessing data set (DB), extracting the data
· calculating information to show (query results)
· displaying information to user, usually, in a user-dependent way (HTML resources)
HTTP and HTML are used as interface, merely. The Web 2.0 requires intelligence, a proper set of instruction to react to user input (named Web Application). Moreover,
0.2.3 CMS: Technical Schema
Thus, there are 3 main components in CMS-ready Web Infrastructure:
Three tiers:
- Presentation: Front-End, user interface
- Services: Middle-End, communication (the logic)
- Back-End Applications: DB (the data set)
0.3 CMS Selection Criteria
Before starting building up a web-site, a CMS product should be choosen because it allows webmasters to operate easier.
0.3.1 CMS Working
CMS Functionality: Building and Updating Web-Site dynamically, without:
· HTML programming
· Server-side Language (PHP, Java, .Net) Programming
· DB designing and deploying
Moreover, the CMS allows dealing with today issues (both technical and social):
- Responsiveness: different display (PC, SmartPhone, TouchScreen, etc) and new technologies (wearable technologies, Internet of Things)
- Social-Ready: user interaction (blog, forum, wiki, etc)
- Fulfillness: augmented content types (docs, photos, images, video, audio, presentation, messages, etc)
0.3.2 CMS Foreword
The CMS acts like an un-coupling element, described by the following characteristics:
· Who: users and web-master
· What: Technology Set
· Why: Social and Collaboration
· Where: Open Media
· When: need resource for managing, info, contents, relations
0.3.3 CMS Usability
The right CMS should be chosen considering also the following characteristics:
· Popularity: numbers of implementation worldwide (usually measured in downloads)
· License: Type of License (GPL, commercial, Free, etc)
· Site: usual sites adopting it (“most used for”)
· Update Frequency: healthiness of the project
· Themes: number of available themes (possibly free)
· Plugins: number of available extension plugins (possibly free)
· Installation: time required for installation
· Moderation: easiness of moderation
· Required Skill: easiness of day-by-day management
· Vulnerability: numbers of important vulnerability found
0.4 CMS Selection
The following paragraphs try to depict CMS concepts, using a three step top-down approach from higher level to lower one:
· Strategical (summary): CMS Customization
· Tactical (view). Full CMS Advanced Functionalities
· Operational (usability): CMS Solutions
0.4.1 Strategical: CMS Customization
The CMS should be properly customized, based on the web-site to be created.
|
Site Type |
Description |
CMS Func |
Writer |
Contribution |
Topic |
Filtering |
|
Blog |
Provide a place in which post messages and comments on these. Tool for creating focused, highly engaing and relevant content |
Blog Photo Gallery |
User |
Individual |
Free |
Moderator |
|
Community |
Provide a place in which post articles and comments about detailed stuff |
Forum Photo Gallery |
User |
Ensuing |
Fixed |
Moderator |
|
Magazine |
Public and General Purposes. |
Article |
Publisher |
Individual |
Fixed |
Redaction |
|
Company |
Provide information to the public about the company. |
ShowCase Multi-Language |
WebDesigner |
Individual |
Many |
|
|
Portal |
Horizontal: common platform for several companies Vertical: specialized entry-point to a specific market |
Multi-Site Multi-Language |
WebDesigner |
Individual |
Fixed |
N/A |
|
e-Shop |
Trading in products or services using computer networks |
e-Commerce |
WebDesigner |
Individual |
N/A |
N/A |
|
Encyclopedia |
reference work or compendium holding a comprehensive summary of information from either all branches of knowledge or a particular branch of knowledge |
Wiki |
User |
Collective |
Fixed |
Merging |
The following table compare the usual different functions:
|
Function |
Examples |
Needs |
SW Modules |
|
Blog |
Diary (personal). |
SEO Scalpel: knowledge of SEO labor intensive innovation, imagination |
Text Management User Management Posting tools SERPS |
|
Forum |
Topic management (company): large amounts of vaguely niche oriented content. |
SEO Broadsword: active community regular moderation |
Text Management User Management Posting tools User Profiling (writer, moderator, etc) |
|
Article |
Publish articles and (eventually) comments on these. |
Labor Intensive Linkage (Mnemonic) |
Text Management Picture Management Posting Tools |
|
ShowCase |
Single umbrella containing: Homepage Navigation Bar Look and Feel About us |
Uniforming Tool |
Text Management Picture Management |
|
Multi-Site Multi-Language |
Specially designed Web page which brings information together from diverse sources in a uniform way.
|
Get information from different sources Put uniform shape (‘metaphor’, based on user) |
Portlet Search API User Mgmt |
|
e-Commerce |
Trading in products or services using computer networks |
Online Shopping Online Marketplace PCI-DSS |
B2B EDI |
|
Wiki |
reference work or compendium holding a comprehensive summary of information from either all branches of knowledge or a particular branch of knowledge |
Post Management |
Wiki User Management (contributor, moderator, etc) Picture Management Text Management |
There are 3 ways for customizing CMS, choosing SW infrastructure of different kinds:
- Open Source: the architecture could be changed, putting on additional modules. Usual example: WordPress, Joomla!, Drupal
- Specialized CMS: no change should be done in order to address specific objectives. Usual example: Vignette, Spin&Go
- Custom CMS: designed and deployed on the basis of hosted content, by the means of huge consulting projects. Usual example: WebLogic, WebSphere
0.4.2 Tactical: Full CMS Functionalities
The following table compares advanced technical aspects:
|
Function |
Description |
|
Time to Market |
Time to deploy the new site |
|
Usage Easiness |
Employable Of-the-Shelf. Easy of use and reduced number of personnel to publish new contents |
|
Huge Community |
Blogs, Forums and Groups or searching on-line about technical issues and their resolutions |
|
Themes and Layouts |
Availability of already developed components |
|
Plug-ins & Modules |
Availabilty of plug-ins, modules and widget to extend the functionalities |
|
Social Networking |
Integration with most common social (e.g. Facebook, Twitter, Linked-In, etc) |
|
SEO Oriented |
Able to build SEO site (easily analysed anarchived by Google, Badoo and Bing):
|
|
Content Strategy/Organization |
Useful to manage intended content (as adopted communication model). Powerful Taxonomy, Ability to Tag: Categorize and Organize complex content |
|
Completeness/Poweness |
Capable of producing most advanced sites |
|
Workflow |
Providing the needed approval and control infrastructural functions |
|
Concept |
Availability of Themes and Layouts |
|
Security |
Mode of addressing security issues |
The data are collected and re-arranged from [15].
0.4.3 Operational: CMS Solutions
According to [11], the top three used product are: WordPress, Joomla! and Drupal. Everyone of these has proper pros and cons. The following graph depicts CMS usage during 2014, according to WebcomWebsites (see [7]):
Figure 2- Top CMS used in 2014
0.5 Top 3 CMS Comparison
A comparison should be performed on the top 3 CMS as these cover up to 70% of the dynamic web sites.
0.5.1 Top 3 CMS Comparison
This document refers to the current versions and their known updates (if available). The following table summarizes a comparison about the “intensive” characteristics of the most popular CMS:
|
WordPress |
Joomla |
Drupal |
|
|
Language |
PHP |
PHP |
PHP |
|
DB |
MySQL |
MySQL |
MySQL |
|
Started |
2003 |
2005 |
2001 |
|
Site |
|||
|
MarketShare |
61% |
7% |
6% |
|
Aim |
Blog, Easy |
Social |
Powerness |
Data are collected from [14] and self-made controlling.
0.5.2 Top 3 CMS covering of Functionalities
More specifically, the advanced functions that are currently enabled are shown in the following table:
|
Function |
WordPress |
Joomla! |
Drupal |
|
Time to Market |
|
|
|
|
Usage Easiness |
|
|
|
|
Huge Community |
|
|
|
|
Themes and Layouts |
|
|
|
|
Plug-ins & Modules |
|
|
|
|
Social Networks |
|
|
|
|
SEO Oriented |
|
|
|
|
Content Strategy/Organization |
|
|
|
|
Completeness/Powerness |
|
|
|
|
Workflow |
|
|
|
|
Scalability |
|
|
|
|
Security |
|
|
|
0.5.3 Top 3 CMS Usability Table
The following table compares more usability-driven aspects of the top 3 CMS products:
|
|
WordPress |
Joomla |
Drupal |
|
Popularity (million download) |
140 |
30 |
15 |
|
License |
GPLv2 |
GPLv2 |
GPLv2 |
|
Language |
PHP |
PHP |
PHP |
|
DB |
MySQL MariaDB |
MySQL MariaDB PostGreSQL MSSQL SQLLite |
MySQL MariaDB PostGreSQL MSSQL SQLLite Oracle |
|
Usual Top Sites |
Commercial |
e-Commerce |
Government |
|
Free Themes |
2000 |
||
|
Free Plugins |
27000 |
7000 |
24000 |
|
Installation Time (min) |
5 |
10 |
10 |
|
Easy of Moderation |
Difficult |
Medium |
Simple |
|
Required Skill |
Low |
Medium |
High |
|
Update Period (days) |
42 |
36 |
51 |
|
High Vulnerablities (since 2005) |
35 |
35 |
12 |
|
High Vulnerability Period (mounth) |
3.5 |
3.5 |
10 |
|
Intended Aims |
Blog Management Textual Content |
CMS Framework |
CMS Framework |
|
Functionalities |
6/11 |
4/11 |
9/11 |
|
Version |
4.1.1 |
3.40 |
7.36 |
The data are collected from [13] and [14].
0.6 CMS used by famous organizations
In the last months, many Education, Government and Political website were migrated from Joomla! To Drupal. Of 10 Top popular WebSites using Joomla! (see [8]) only 6 out of 10 (60%) are effectively using Joomla!, nowadays: 2 WebSite have migrated to Drupal, 2 one to WordPress and 1 is adopting another CMS mechanism. Moreover, the page “10 Most Popular Web Site using Joomla!” is not updated from 3 years (so, what about the software in itself?).
0.6.1 Drupal
Here the organizations that have chosen Drupal:
|
Institution |
Type |
URL |
CMS |
|
CERN |
Research |
Drupal |
|
|
NASA |
Government |
Drupal |
|
|
US-CERT |
Government |
Drupal |
|
|
WhiteHouse |
Government |
Drupal |
|
|
Homeland Security |
Government |
Drupal |
|
|
British Council |
Government |
Drupal |
|
|
Task Force on Childhood Obesity |
Government |
Drupal |
|
|
US Department of Education |
Government |
Drupal |
|
|
World Food Programme |
Government |
Drupal |
|
|
Agenzia Spaziale Italiana |
Government |
Drupal |
|
|
Cambridge |
University |
Drupal |
|
|
Oxford |
University |
Drupal |
|
|
Harward |
University |
Drupal |
|
|
Michigan |
University |
Drupal |
|
|
Arizona |
University |
Drupal |
|
|
CyberLaw Standford |
University |
Drupal |
|
|
Cornell Library |
University |
Drupal |
|
|
Sapienza |
University |
Drupal |
|
|
CIS |
University |
Drupal |
|
|
LUISS |
University |
Drupal |
|
|
LUMSA |
University |
Drupal |
|
|
SkyBox |
Private Company |
Drupal |
|
|
RedHat |
Private Company |
Drupal |
|
|
LinuxFoudation |
Research |
Drupal |
|
|
The Economist |
NewsPaper |
Drupal |
|
|
The Hill |
NewsPaper |
Drupal |
“Drupal powers twice as many federal government websites as every other CMS combined. That’s more than six Drupal sites for every one WordPress.” [Benjamin Balter, US E-Government and Federal IT Team, Executive Office of the President]. More information on [19].
0.6.2 Other OpenSource
Here some organization that have choosen another OpenSource (GPL) CMS solution:
|
Institution |
Type |
URL |
CMS |
|
ENISA |
Government |
Plone |
|
|
NIST |
Government |
e017 |
|
|
OWASP |
Research |
MediaWiki |
|
|
Linux.org |
Research |
XenForo |
|
|
SlideShare |
Private Company |
Ruby on Rails |
|
|
Linux.com |
Private Company |
Joomla! |
|
|
NotreDame |
University |
Joomla! |
|
|
ITWire.com |
e-Commerce |
Joomla! |
|
|
Guggenheim |
Private Company |
Joomla! |
|
|
MTV Greece |
Private Company |
Joomla! |
|
|
UNRIC |
Government |
Joomla! |
|
|
TamTamy |
Private Company |
WordPress |
|
|
IlFattoQuotidiano |
NewsPaper |
WordPress |
|
|
RomaOstia |
Sport |
WordPress |
|
|
SuSe (Novell) |
Private Company |
WordPress |
|
|
The Fashion Spot |
e-Commerce |
WordPress |
|
|
Singolarity |
University |
WordPress |
0.6.3 Commercial
Here some organization that have choosen to use a commercial solution
|
Institution |
Type |
URL |
CMS |
|
NSA |
Government |
ASP.Net |
|
|
London City |
University |
Squiz Matrix |
|
|
Statale Milano |
University |
OpenText |
|
|
Bocconi |
University |
IBM WebSphere |
|
|
Torvergata |
University |
IBM WebSphere |
|
|
Maratona di Roma |
Sport |
Plesk |
|
|
Splunk |
Private Company |
Adobe CQ5 |
|
|
Financial Times |
NewsPaper |
Méthode (EidosMedia) |
|
|
Washington Post |
NewsPaper |
Méthode (EidosMedia) |
|
|
Il Sole 24 Ore |
NewsPaper |
Méthode (EidosMedia) |
|
|
Corriere della Sera |
NewsPaper |
Méthode (EidosMedia) |
|
|
AdnKronos |
NewsPaper |
Méthode (EidosMedia) |
|
|
La Stampa |
NewsPaper |
Méthode (EidosMedia) |
0.7 References
|
[11] |
Usage of CMS for WebSite: http://w3techs.com/technologies/overview/content_management/all |
|
[12] |
Market Share Trends: http://w3techs.com/technologies/history_overview/content_management |
|
[13] |
CMS Comparison Chart: http://websitesetup.org/cms-comparison-wordpress-vs-joomla-drupal/ |
|
[14] |
CMS Comparison: http://www.rackspace.com/knowledge_center/article/cms-comparison-drupal-joomla-and-wordpress |
|
[15] |
Side by Side Comparison: http://www.rackspace.com/knowledge_center/article/cms-comparison-drupal-joomla-and-wordpress |
|
[16] |
Vulnerability DB: https://www.vulnerabilitycenter.com |
|
[17] |
Webcom Website 2014 statistic: |
|
[18] |
Top 10 popular WebSites using Joomla!: http://magazine.joomla.org/issues/issue-july-2012/item/800-10-most-popular-websites-using-Joomla |
|
[19] |
Who use Drupal: |
|
[20] |
Web Content Management System: |